Cybersecurity solutions are a collection of tools, strategies, and practices designed to safeguard digital information, systems, and networks from malicious cyber activities. With the surge in data-driven applications, cloud adoption, and remote work, the risk landscape for organizations and individuals has expanded significantly, making cybersecurity not only necessary but integral to modern business practices. This article delves into the essential components, types, benefits, and latest advancements in cybersecurity solutions, emphasizing their importance in the evolving digital landscape.
Understanding Cybersecurity Solutions
In a digital world where data is as valuable as currency, cybersecurity solutions have become essential for safeguarding both personal and organizational assets. Cybersecurity solutions refer to the suite of tools, technologies, policies, and practices developed to protect systems, networks, and data from malicious attacks, unauthorized access, and other cyber threats. These solutions create a protective barrier around digital infrastructure, enabling organizations and individuals to operate securely in an increasingly online landscape.
To understand cybersecurity solutions, it is crucial to recognize the various types of threats they combat and the comprehensive strategies used to counter these threats. Cybersecurity solutions work on multiple levels, each focused on different aspects of protection, from network security and application defense to data protection and threat intelligence.
I. The Importance of Cybersecurity Solutions
The growth of cyber threats has made cybersecurity a top priority for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. Cyber threats encompass a variety of risks, such as malware, ransomware, phishing, denial-of-service attacks, and more advanced strategies like social engineering. As organizations increasingly move to the cloud and adopt remote working models, their attack surfaces (or potential points of vulnerability) grow, increasing the risk of data breaches, operational downtime, and financial losses.
The impact of cyber-attacks is far-reaching:
- Data Breaches: Loss or theft of sensitive data can lead to regulatory fines, reputation damage, and costly recovery efforts.
- Operational Disruptions: Cyber incidents can paralyze essential services and workflows, leading to productivity loss.
- Financial Losses: Ransom payments, legal fees, and compensation costs can drain an organization’s resources.
- Reputation Damage: Trust is hard-won and easily lost; a single breach can severely damage an organization’s credibility.
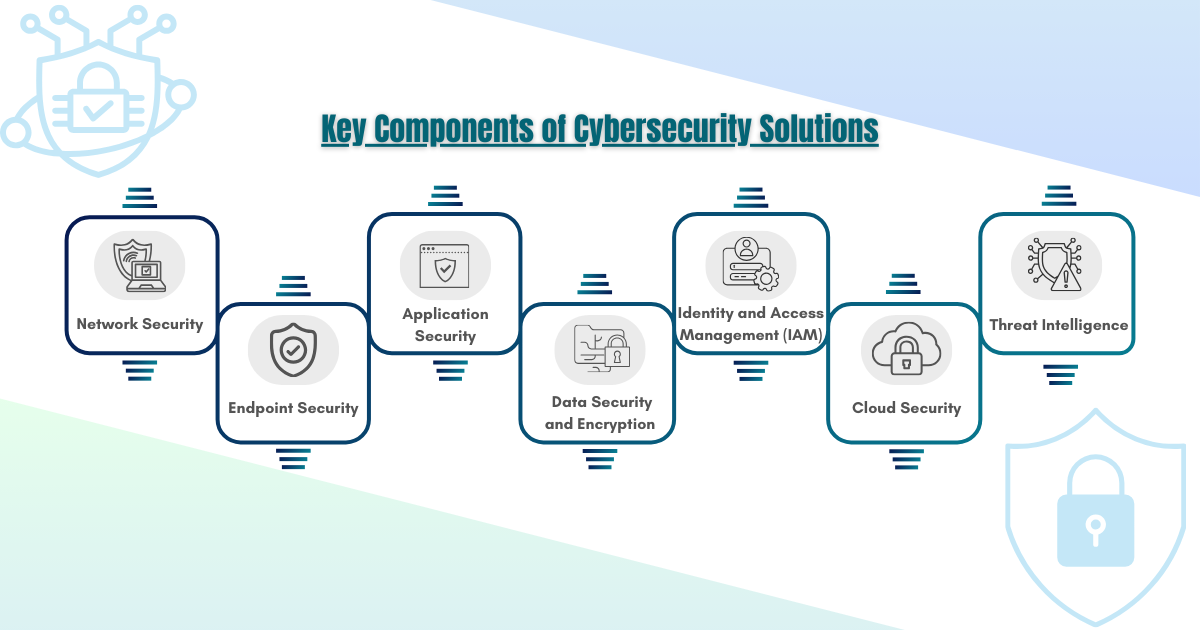
II. Key Components of Cybersecurity Solutions
To establish a resilient cybersecurity framework, organizations and individuals must implement a comprehensive suite of components. Key aspects include:
a. Network Security: Safeguards the integrity of network infrastructure against unauthorized access, misuse, or malfunctions. Network security includes firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and network segmentation to reduce potential attack surfaces.
b. Endpoint Security: Aims to protect end-user devices, including computers, laptops, and mobile devices. Endpoint security solutions typically include antivirus software, endpoint detection and response (EDR), and mobile device management (MDM) to monitor device health and enforce security policies.
c. Application Security: Ensures that applications are secure from potential vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit. This involves coding best practices, regular vulnerability assessments, and application firewalls to shield applications from threats.
d. Data Security and Encryption: Protects data integrity and confidentiality by employing encryption protocols, data masking, tokenization, and secure data storage methods. Strong data security practices prevent unauthorized access and reduce the risk of data breaches.
e. Identity and Access Management (IAM): Manages user access and privileges within an organization’s network, often using multi-factor authentication (MFA), single sign-on (SSO), and identity governance to enforce access policies.
f. Cloud Security: Addresses risks associated with cloud computing environments, covering data protection, access controls, and compliance across multi-cloud or hybrid environments. Cloud security solutions often include cloud access security brokers (CASBs) and cloud workload protection platforms (CWPPs).
g. Threat Intelligence: Provides insights into the current threat landscape and specific cyber risks facing an organization. Threat intelligence solutions analyze and share information about emerging threats, vulnerabilities, and tactics used by attackers, enabling proactive defenses.
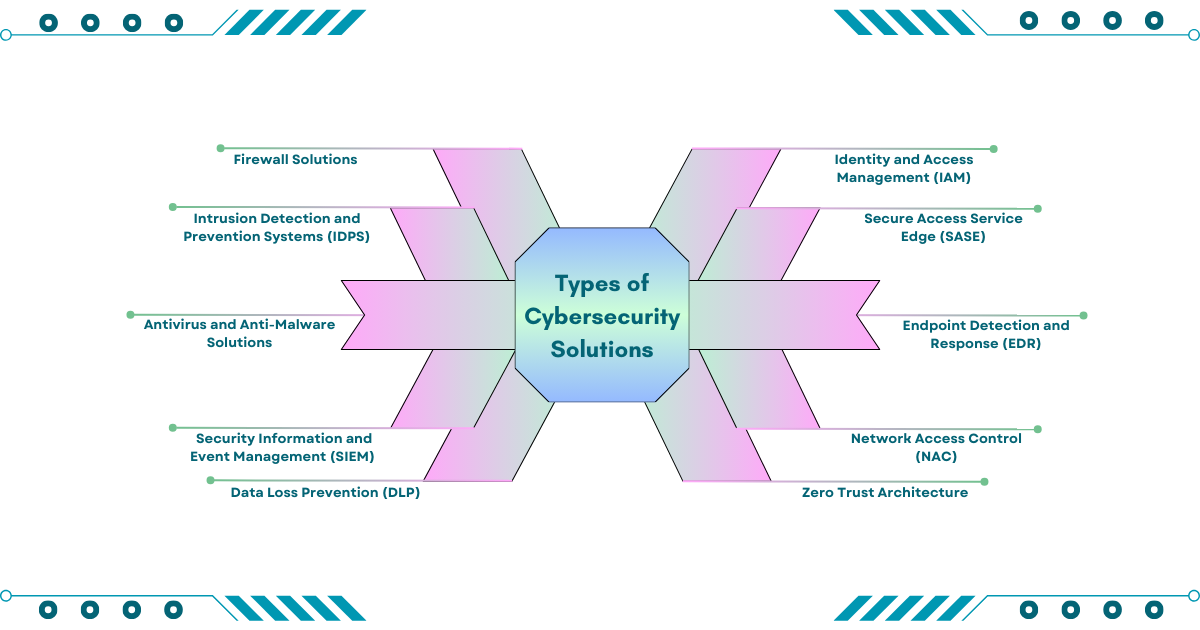
III. Types of Cybersecurity Solutions
Cybersecurity solutions vary in complexity and functionality, tailored to different threat vectors. Here are some key types:
♦ Firewall Solutions
Firewalls monitor and control network traffic, allowing only trusted data packets through. Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) offer advanced features like deep packet inspection (DPI) and integration with threat intelligence sources.
♦ Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
Detect and respond to potential threats within the network. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) alert administrators to suspicious activities, while intrusion prevention systems (IPS) actively block malicious traffic.
♦ Antivirus and Anti-Malware Solutions
Essential for endpoint security, these solutions scan for, detect, and remove malicious software from systems. Modern antivirus solutions incorporate behavioral analysis to detect zero-day threats.
♦ Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
Combines real-time monitoring, event logging, and analysis to detect unusual patterns and respond to security incidents. SIEM solutions provide a centralized view of network activity, allowing faster and more informed responses.
♦ Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Prevents sensitive data from being accessed, shared, or removed by unauthorized users. DLP solutions protect data at rest, in transit, and in use, ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations.
♦ Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM solutions provide tools to control who can access resources, enforce access policies, and manage user identities. They often incorporate authentication factors like passwords, biometrics, and tokens.
♦ Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
A relatively new model, SASE combines network security functions like secure web gateways (SWG), CASB, and ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access) with WAN capabilities to provide secure, low-latency access to cloud applications.
♦ Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
EDR solutions provide continuous monitoring of endpoint activities to identify and address potential threats. These systems often use AI to recognize abnormal behaviors and can isolate compromised devices automatically.
♦ Network Access Control (NAC)
Limits access to the network based on device compliance with security policies, helping to prevent unauthorized devices from connecting to the network.
♦ Zero Trust Architecture
Zero trust cybersecurity approaches trust no device or user by default, enforcing continuous authentication and validation at every network access point.
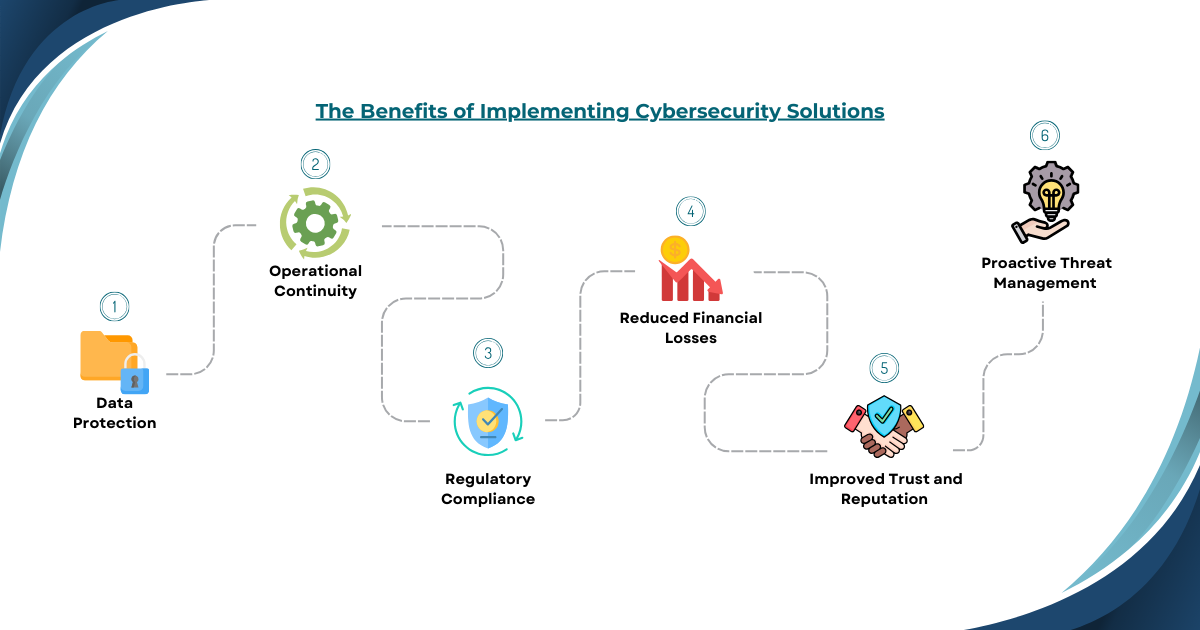
IV. The Benefits of Implementing Cybersecurity Solutions
Cybersecurity solutions bring numerous advantages to both individuals and organizations, including:
1. Data Protection: Robust cybersecurity measures prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data, reducing the risk of data breaches and the potential for data loss.
2. Operational Continuity: By preventing cyber-attacks, organizations can ensure their operations run smoothly without disruptions, safeguarding revenue streams and maintaining customer trust.
3. Regulatory Compliance: Many industries have strict cybersecurity regulations. Implementing cybersecurity solutions helps organizations comply with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA, avoiding hefty fines and reputational damage.
4. Reduced Financial Losses: Cyber-attacks can result in substantial financial damages from lost revenue, legal expenses, and compensation for affected customers. Effective cybersecurity minimizes these risks.
5. Improved Trust and Reputation: A strong cybersecurity posture builds trust with clients, partners, and stakeholders, enhancing the organization’s reputation as a secure and reliable entity.
6. Proactive Threat Management: With real-time monitoring and threat intelligence, cybersecurity solutions enable organizations to detect and mitigate threats proactively, reducing the impact of potential attacks.
V. Key Trends in Cybersecurity Solutions
As cyber threats evolve, cybersecurity solutions must adapt and innovate to stay ahead. Here are some current trends shaping the future of cybersecurity:
» Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are enhancing the effectiveness of cybersecurity solutions by analyzing massive datasets to detect anomalies and predict potential threats. AI-driven solutions can respond faster than traditional methods, reducing the time attackers have to exploit vulnerabilities.
» Zero Trust Security Models
The zero trust model, which treats every user and device as untrustworthy until verified, is gaining traction. Organizations are implementing zero trust architectures to improve security by requiring continuous authentication.
» Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
XDR unifies multiple security products (SIEM, EDR, and NDR) under a single platform to improve detection and response capabilities across endpoints, networks, and applications.
» Cloud-Native Security
As cloud adoption grows, cloud-native security solutions provide flexible, scalable security for cloud environments. These solutions are often integrated into cloud platforms, making them easier to deploy and manage.
» Automation and Orchestration
Security automation tools handle repetitive tasks and incident responses, freeing up analysts to focus on more complex challenges. Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) platforms streamline workflows and reduce response times.
» Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs)
These technologies help organizations protect sensitive data during processing. PETs include encryption, anonymization, and secure multi-party computation, allowing companies to analyze data without compromising privacy.
» Biometric Security
Biometric authentication, such as fingerprint and facial recognition, is becoming common for secure access, particularly in mobile devices and high-security environments.
» Behavioral Biometrics
This approach uses behavioral analysis to verify identity, analyzing factors like typing speed, mouse movement, and navigation patterns to detect suspicious behavior.
» Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography, though still in its early stages, promises a new level of security by leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics to create virtually unbreakable encryption.
VI. Implementing Cybersecurity Solutions: Best Practices
Deploying cybersecurity solutions effectively requires strategic planning, continuous monitoring, and adherence to best practices. Key recommendations include:
1. Conduct Risk Assessments: Regularly assess risks to identify potential vulnerabilities and prioritize security investments based on the specific needs of your organization.
2. Implement a Layered Security Approach: Layered security, also known as defense-in-depth, provides multiple defenses at various levels, making it harder for attackers to succeed.
3. Stay Updated with Patches: Ensure that all software, systems, and applications are kept up-to-date with the latest security patches to reduce vulnerabilities.
4. Educate Employees: Cybersecurity training for employees is crucial to prevent social engineering attacks, such as phishing, which often target human vulnerabilities.
5. Develop an Incident Response Plan: Create a robust incident response plan to handle potential breaches, including roles, communication protocols, and recovery steps to minimize damage.
6. Implement Strong Access Controls: Use IAM solutions to enforce strong access controls, limiting data access based on role, responsibilities, and need-to-know principles.
7. Embrace Threat Intelligence: Utilize threat intelligence services to stay informed about emerging threats, enabling proactive adjustments to security strategies.
8. Leverage Security Automation: Automate routine security tasks with SOAR tools to optimize resource use and respond to threats more effectively.
9. Monitor Continuously: Continuous monitoring of network activity and endpoints helps detect and respond to threats in real time, preventing minor issues from escalating.
VII. Future of Cybersecurity Solutions
The cybersecurity landscape will continue to evolve as new technologies, such as 5G, Internet of Things (IoT), and edge computing, introduce additional security challenges. The future of cybersecurity solutions will likely focus on:
• Integrating AI with XDR and SOAR Platforms
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) with Extended Detection and Response (XDR) and Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platforms represents a significant advancement in the cybersecurity landscape. By leveraging AI, these platforms can enhance threat detection, response times, and resource efficiency, creating a unified, automated approach to security management that is both proactive and scalable.
• Quantum-Resistant Cryptography
As quantum computing continues to advance, its potential impact on current cryptographic systems becomes a serious concern. Classical encryption algorithms like RSA, DSA, and ECC, which are foundational to securing communications, digital signatures, and financial transactions, may soon be vulnerable to quantum attacks. Quantum-resistant cryptography, also known as post-quantum cryptography (PQC), aims to develop new cryptographic algorithms that remain secure even in the face of quantum computing’s unprecedented computational power. This shift is crucial to future-proofing cybersecurity, ensuring that sensitive data remains protected from potential quantum threats.
• Privacy-First Cybersecurity
With the exponential growth of data generation and the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, privacy-first cybersecurity has emerged as a crucial approach to protecting individual and organizational data. Privacy-first cybersecurity emphasizes not only safeguarding data from malicious attacks but also respecting and preserving user privacy at every stage. In this approach, data protection goes beyond merely complying with regulations; it becomes an integral part of security infrastructure and system design. This shift is essential in building trust with users, adhering to regulations like GDPR and CCPA, and ensuring long-term digital resilience.
•Collaboration Between Public and Private Sectors
The complexity of today’s cyber threats requires a united response, combining resources and expertise from both the public and private sectors. Collaboration between governments, private companies, and other stakeholders has become essential to enhance cybersecurity resilience on a global scale. By working together, these sectors can create a more robust defense infrastructure, share critical threat intelligence, and establish standardized practices that protect citizens, businesses, and national security interests alike.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity solutions are essential for protecting today’s interconnected digital environment from an ever-growing range of threats. A well-rounded cybersecurity strategy incorporates multiple tools and practices, from firewalls and antivirus software to advanced solutions like zero trust architectures and AI-driven threat detection. As cyber threats continue to evolve, organizations must stay vigilant, adapt to new security challenges, and prioritize cybersecurity as a critical component of their digital infrastructure. By embracing the latest technologies and following best practices, individuals and organizations can safeguard their data, maintain operational continuity, and build trust in the digital ecosystem.