
The world of technology is constantly evolving, and one of the most exciting and influential changes in recent years has been the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) automation. AI automation is a broad term that refers to using machines and computer programs to carry out tasks without requiring human input. It’s shaping industries, enhancing efficiency, and giving businesses new ways to operate smarter. But what does that mean for professionals, businesses, and the world? In this article, we’ll dive into what AI automation is, how it works, and the impact it’s having on the modern workplace.
What Is AI Automation?
AI automation refers to the use of artificial intelligence to automate tasks. It combines two major technological forces: AI, which refers to machines that can “think” like humans, and automation, which involves systems that can perform tasks without human intervention. Together, these technologies create solutions that can complete tasks quickly, accurately, and consistently.
Imagine you’re running a business. Traditionally, certain tasks, like answering customer queries or sorting data, might require a dedicated person or team. With AI automation, machines can now take over these tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on higher-level activities. Whether it’s responding to emails, analyzing data, or even managing parts of the supply chain, AI automation is capable of doing these jobs efficiently.
The Rise of AI Automation
AI automation has grown in popularity for several reasons. One key factor is the ability of AI to learn and improve over time. This means that machines aren’t just carrying out tasks—they’re getting better at them the more they do it. This “learning” ability enables businesses to trust that the machines will continue to improve, making fewer mistakes and processing more information as time goes on.
Another driving force behind the rise of AI automation is the increase in computing power and the availability of data. Businesses now generate more data than ever before, and analyzing this information manually is nearly impossible. AI automation steps in to process and analyze large amounts of data quickly, allowing businesses to make informed decisions faster.
Furthermore, there has been a push for companies to become more efficient, cut costs, and improve customer service. AI automation answers these needs by offering solutions that can work around the clock, reduce human error, and speed up operations.
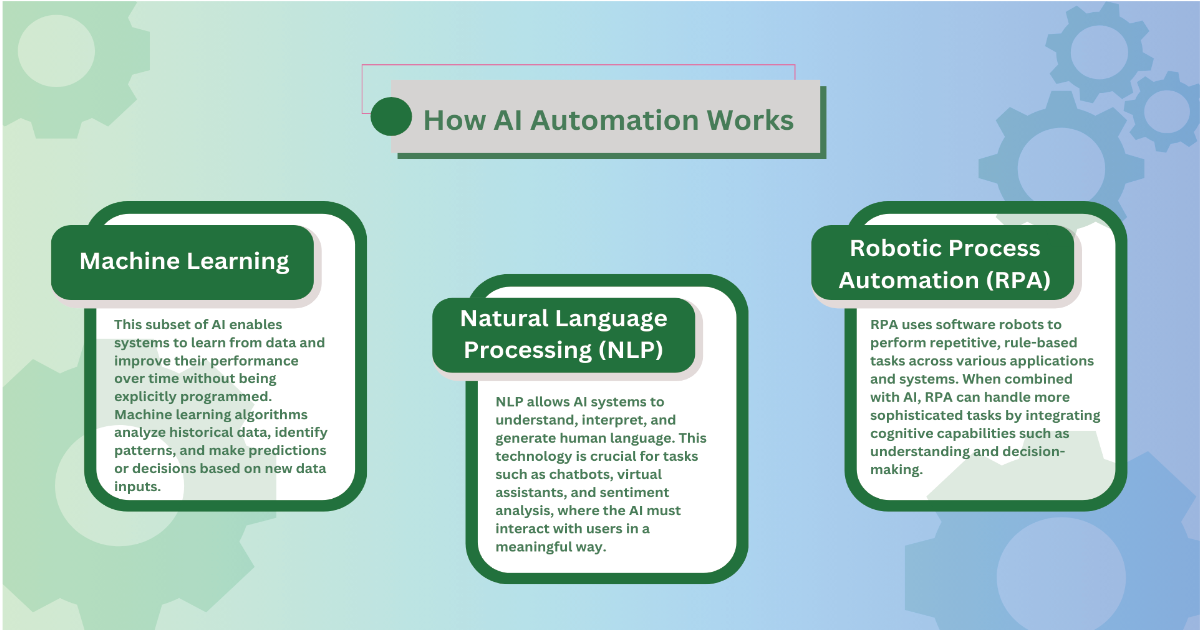
The Benefits of Automation
Automation, the use of technology to perform tasks that were previously done by humans, has become a cornerstone of modern industries. From manufacturing lines to software applications, automation offers a plethora of benefits that enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall productivity. Here’s a look at some of the key advantages of automation.
a. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
One of the most significant benefits of automation is its ability to dramatically increase efficiency and productivity. Automated systems can execute repetitive tasks more quickly and accurately than humans. For instance, in manufacturing, robots can work around the clock without breaks, leading to higher output and faster production times. In the software realm, automated processes can handle data entry, reporting, and other routine tasks swiftly, freeing up human workers to focus on more complex and strategic activities. This boost in productivity not only helps businesses meet growing demands but also allows for the optimization of resources
b. Cost Reduction
Automation can lead to substantial cost savings. By minimizing reliance on manual labor, companies can reduce their operational costs. Automation also minimizes errors that can be costly to correct. For example, in financial services, automated systems can handle transactions and data processing more accurately than manual methods, reducing the risk of costly mistakes. Additionally, automation often requires a significant upfront investment, but the long-term savings in labor costs and error correction can far outweigh the initial expenditure.
c. Enhanced Quality and Consistency
Consistency in product quality is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction and brand reputation. Automated systems can deliver consistent results, ensuring that products or services meet predefined standards. In manufacturing, automation helps maintain uniformity in production, reducing variations and defects. In the service industry, automated tools can standardize responses and processes, leading to a more reliable customer experience. This consistency not only enhances the quality of output but also builds trust with customers.
d. Improved Safety
Automation can significantly improve workplace safety by taking over dangerous or hazardous tasks. In industries such as mining, construction, and chemicals, automation can handle tasks that pose risks to human workers. For example, robotic systems can perform tasks in toxic environments, reducing the likelihood of accidents and health issues among employees. This shift not only protects workers but also reduces the costs associated with workplace injuries and insurance claims.
e. Scalability and Flexibility
Automation enables businesses to scale and adapt to evolving market conditions. Automated systems can be easily adjusted to handle varying levels of production or service demands. For instance, an e-commerce platform can use automated inventory management systems to adjust stock levels based on real-time sales data. This flexibility allows businesses to respond quickly to market trends and consumer preferences without the need for extensive manual adjustments.
f. Better Data and Analytics
Automation facilitates the collection and analysis of data, providing businesses with valuable insights. Automated systems can track and analyze performance metrics, customer behaviors, and operational efficiency, helping companies make informed decisions. For example, marketing automation tools can provide detailed reports on campaign effectiveness, allowing businesses to optimize their strategies and improve ROI. Enhanced data analytics also enable companies to identify trends, forecast demands, and make strategic adjustments.
e. Increased Innovation
By automating routine tasks, organizations can free up human resources for more creative and innovative endeavors. Employees are no longer bogged down by mundane tasks and can focus on developing new ideas, products, or services. This shift fosters a culture of innovation, as teams are better positioned to explore new opportunities and drive growth. Automation, therefore, not only improves operational efficiency but also contributes to the long-term success and competitiveness of businesses.
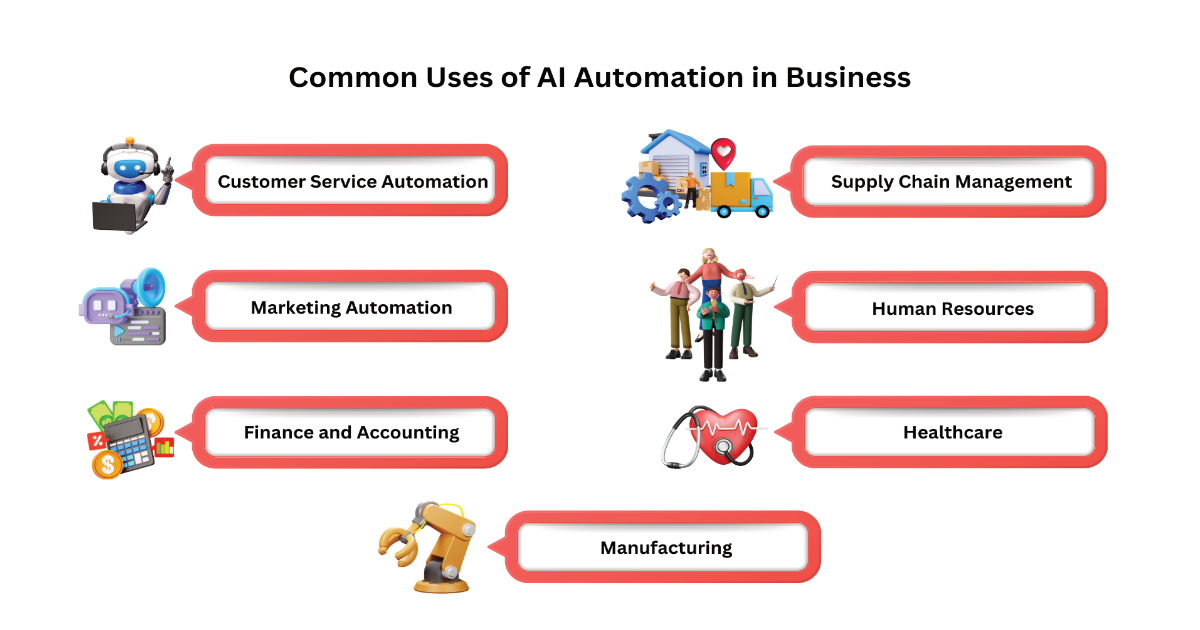
Common Uses of AI Automation in Business
AI automation is being adopted across a variety of industries, transforming the way businesses operate. Here are some of the most common applications:
1. Customer Service Automation
One of the most visible forms of AI automation is in customer service. Chatbots and virtual assistants are now commonplace on websites and mobile apps, handling customer inquiries without needing human assistance. They can respond to frequently asked questions, process orders, and even troubleshoot basic problems.
2. Marketing Automation
AI has revolutionized digital marketing by automating tasks like email campaigns, social media posting, and targeted ads. AI automation tools can analyze consumer behavior and market trends, creating personalized marketing strategies tailored to individual customers. This results in more effective campaigns and higher conversion rates.
3. Finance and Accounting
In the financial world, AI automation helps with everything from processing invoices to analyzing financial reports. AI can quickly identify patterns in financial data, predict future trends, and detect anomalies that could indicate fraud. It streamlines the accounting process and reduces the risk of errors.
4. Supply Chain Management
AI automation is helping businesses optimize their supply chains by predicting demand, tracking shipments, and managing inventory. These systems can anticipate shortages, suggest the most efficient shipping routes, and automate warehouse operations to ensure timely deliveries.
5. Human Resources
HR departments are using AI to automate recruiting, screening, and onboarding processes. AI-powered platforms can analyze resumes, conduct initial interviews, and even assess candidates’ qualifications based on predefined criteria. This saves time and ensures that businesses hire the best talent for the job.
6. Healthcare
In healthcare, AI automation is being used to assist in diagnostics, manage patient records, and even predict potential health issues before they arise. For example, AI-powered tools can scan medical images for signs of disease, reducing the burden on doctors and improving patient outcomes.
7. Manufacturing
AI automation in manufacturing involves the use of robots and AI systems to oversee production lines. These machines can work with precision, perform quality control, and even carry out dangerous tasks, all while ensuring minimal downtime and fewer defects in products.
Challenges of AI Automation
While AI automation offers many benefits, it’s not without its challenges. Businesses must be aware of the potential hurdles they may face when implementing AI-powered systems.
a. Cost of Implementation
Although AI automation can save businesses money in the long run, the upfront cost of implementing these systems can be high. Developing AI-powered tools, integrating them into existing operations, and training employees on how to use them may require significant investment.
b. Data Privacy Concerns
AI automation relies heavily on data to function effectively. This can raise concerns about how that data is collected, stored, and used. Companies must take steps to ensure they comply with data privacy laws and protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
c. Job Displacement
One of the most widely discussed concerns regarding AI automation is the fear that it could lead to job displacement. As machines take on more tasks, certain jobs may become redundant. However, many experts argue that while AI will replace certain roles, it will also create new opportunities for workers in areas that require human creativity and problem-solving.
d. Bias in AI Systems
AI systems are only as good as the data they’re trained on. If the data is biased, the AI may produce biased outcomes. This is a challenge that companies must address to ensure that AI-powered systems are fair and inclusive. It requires ongoing monitoring and refinement of the algorithms to prevent unintended outcomes.
The Future of AI Automation
As we move further into the 21st century, artificial intelligence (AI) and automation are poised to transform industries, economies, and societies in unprecedented ways. The future of AI automation holds immense potential, offering both opportunities and challenges. Understanding these developments is crucial for businesses, policymakers, and individuals alike. Here’s a look at what the future might hold for AI automation.
1. Advanced Cognitive Capabilities
The future of AI automation will see the rise of more advanced cognitive capabilities. Current AI systems are proficient at handling repetitive and data-driven tasks, but the next wave of AI will possess enhanced cognitive functions. This includes improved natural language understanding, context-aware reasoning, and the ability to perform complex problem-solving. For instance, AI could revolutionize customer service with advanced chatbots that understand nuanced human emotions and context, providing more personalized and effective interactions.
2. Ubiquitous Automation
AI automation is expected to become ubiquitous across various sectors. In healthcare, AI could automate complex diagnostic processes, enabling early detection of diseases and personalized treatment plans. In finance, AI-driven automation might handle everything from fraud detection to investment strategies. The shift towards ubiquitous automation will lead to more efficient and streamlined operations, but it will also require businesses to adapt to new technologies and integrate them into their existing processes.
3. Human-AI Collaboration
The future will likely see a shift towards more collaborative interactions between humans and AI systems. AI is anticipated to enhance, rather than replace, human workers’ capabilities. For example, in creative fields such as writing or design, AI tools could assist with generating ideas or refining concepts, while human expertise ensures the final product aligns with nuanced objectives and creative vision. This symbiotic relationship will enhance productivity and innovation, leveraging the strengths of both human and machine.
4. Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
As AI automation becomes more pervasive, ethical and regulatory considerations will play a crucial role in shaping its development and deployment. Challenges like data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the effects on employment must be tackled. Ensuring that AI systems operate transparently and fairly will be essential to maintaining public trust. Governments and organizations will need to establish frameworks and guidelines to address these concerns and ensure that AI automation benefits society as a whole.
5. Economic and Workforce Impact
The economic impact of AI automation will be significant, with potential shifts in labor markets and industry structures.Although automation may cause job displacement in some sectors, it also holds the potential to generate new opportunities and industries. For instance, the rise of AI could spur demand for roles in AI development, maintenance, and oversight. To mitigate the negative effects of job displacement, there will be a need for reskilling and upskilling programs to help workers transition into new roles and industries.
6. Enhanced Personalization and User Experience
AI automation will drive significant advancements in personalization and user experience. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI systems can offer highly tailored recommendations and experiences. For example, e-commerce platforms might use AI to provide personalized shopping experiences based on individual preferences and behaviors. Similarly, media and entertainment services could deliver content that aligns with users’ specific interests and viewing habits. This level of personalization will enhance customer satisfaction and engagement.
7. Integration with Emerging Technologies
The integration of AI automation with other emerging technologies will further amplify its impact. For instance, AI combined with Internet of Things (IoT) devices will enable smart homes and cities, where automated systems manage everything from energy consumption to traffic flow. Similarly, AI-powered robotics and automation will transform manufacturing and logistics, leading to more efficient supply chains and production processes. The synergy between AI and these technologies will drive innovation and create new possibilities.
8. Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Future AI systems will be characterized by their ability to continuously learn and adapt. Unlike current systems that require periodic updates, next-generation AI will be capable of real-time learning from new data and experiences. This will enable AI to stay relevant and effective in dynamic environments, responding to changes and evolving needs with greater agility. Continuous learning will enhance the effectiveness of AI automation across various applications, from business processes to everyday life.



