AI in healthcare is transforming the future of medicine by enhancing precision, efficiency, and accessibility. By harnessing machine learning and data analytics, AI can process vast volumes of medical data to enhance diagnostics, optimize treatment plans, and improve patient outcomes. Tools like AI-powered imaging systems enable early detection of diseases such as cancer, reducing errors and facilitating timely interventions.
In personalized medicine, AI tailors treatments based on a patient’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and medical history, ensuring more effective care. Predictive analytics help healthcare providers anticipate disease progression, optimize resource allocation, and prevent critical conditions before they arise. AI also speeds up drug discovery, cutting down both the time and costs required to bring new treatments to market.
Remote monitoring devices, powered by AI, allow real-time health tracking, empowering patients and doctors with proactive care. Additionally, AI-driven telemedicine platforms and virtual assistants are making healthcare more accessible, particularly in underserved areas.
While AI holds immense promise, challenges like data privacy, ethical considerations, and integration with existing systems must be addressed. Moving forward, AI will not replace healthcare professionals but will enhance their capabilities, enabling smarter, faster, and more patient-centric care. AI is paving the way for a future of innovation and improved health outcomes globally.
I. Introduction to AI in Healthcare
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become one of the most revolutionary technologies in the healthcare industry. AI refers to the ability of machines to simulate human intelligence, perform complex tasks, and continuously learn from data. In healthcare, this technology leverages advanced algorithms, machine learning, and deep learning to process massive amounts of medical information and derive actionable insights. From enhancing diagnostics to streamlining administrative tasks, AI has the potential to improve every aspect of healthcare delivery.
The growing availability of electronic health records (EHRs), medical imaging data, and wearable devices has created an enormous reservoir of data that traditional methods struggle to analyze. AI-powered tools can process this data with unprecedented speed and precision, uncovering trends, patterns, and predictions that improve decision-making for clinicians and healthcare systems. For instance, AI algorithms can analyze medical images to detect early signs of diseases like cancer or cardiovascular issues, often with accuracy that matches or exceeds human specialists.
The application of AI in healthcare spans various domains, including diagnostics, treatment planning, drug discovery, patient care, and hospital management. For example, in diagnostics, AI systems can identify abnormalities in radiological scans such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, providing faster and more accurate results than manual reviews. In drug discovery, AI speeds up the identification of new molecules and drug candidates, significantly reducing the time and cost of traditional research and development.
Moreover, AI supports personalized medicine by tailoring treatment plans based on a patient’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and clinical history. This ensures that healthcare interventions are precise, effective, and aligned with individual needs. Virtual health assistants powered by AI further enhance patient engagement by offering 24/7 support, answering medical queries, and assisting with appointment scheduling.
The benefits of AI in healthcare are immense. It improves diagnostic accuracy, enhances operational efficiency, reduces costs, and drives better patient outcomes. By automating repetitive administrative tasks, AI allows healthcare providers to devote more time to delivering patient-centered care. Additionally, AI bridges gaps in healthcare accessibility, particularly in underserved or remote regions, by enabling telemedicine and remote patient monitoring.
Nevertheless, implementing AI in healthcare comes with its own set of challenges. Concerns about data privacy, algorithmic bias, integration with existing systems, and regulatory compliance need to be addressed to ensure safe and ethical implementation. Collaborative efforts between healthcare professionals, AI developers, and policymakers will be essential to overcome these barriers.
In conclusion, AI is not just a technological advancement but a transformative force that holds the potential to redefine healthcare as we know it. As the technology continues to evolve, its role in improving diagnostics, treatment, and patient care will only grow, paving the way for a more efficient, accessible, and patient-centric healthcare system.
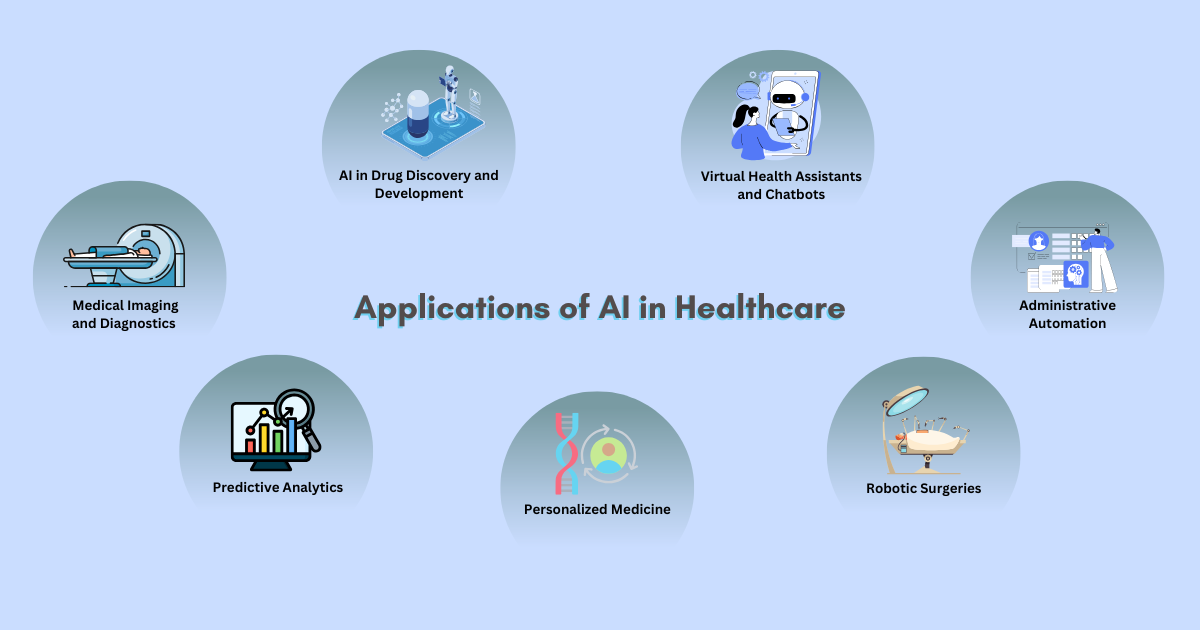
II. Applications of AI in Healthcare
A. Medical Imaging and Diagnostics
AI has made significant strides in medical imaging, enabling faster and more precise diagnoses. AI-powered tools can analyze medical scans like X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to identify anomalies such as tumors, fractures, or internal bleeding.
- Example: AI algorithms like Google’s DeepMind have achieved accuracy rates similar to or even surpassing human radiologists in identifying breast cancer or retinal diseases.
- Benefits: AI reduces human error, speeds up diagnostic timelines, and assists radiologists by prioritizing scans requiring immediate attention.
B. Predictive Analytics
AI helps predict diseases and patient outcomes by analyzing historical data, lab reports, and genetic information.
- Chronic Disease Prediction: AI can predict the onset of chronic diseases like diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, or cancer by analyzing risk factors such as lifestyle, genetics, and medical history.
- Sepsis Prediction: AI models can identify early signs of sepsis in hospitalized patients, enabling timely intervention and reducing mortality rates.
C. AI in Drug Discovery and Development
Drug development is a time-consuming and expensive process. AI accelerates this process by analyzing molecular structures, simulating drug interactions, and identifying potential drug candidates.
- Example: AI systems, such as those developed by BenevolentAI and Insilico Medicine, have helped identify drug molecules in record time.
- Benefits: AI reduces the timeline for drug discovery from years to months, lowers R&D costs, and increases the likelihood of successful outcomes.
D. Personalized Medicine
AI enables personalized treatment plans tailored to an individual’s genetic profile, lifestyle, and medical history.
- Genomic Medicine: AI systems analyze genetic data to predict an individual’s susceptibility to diseases and recommend targeted treatments.
- Precision Oncology: AI algorithms suggest the most effective cancer treatments based on a patient’s genetic makeup and tumor characteristics.
E. Virtual Health Assistants and Chatbots
AI-powered virtual assistants and chatbots offer 24/7 support to patients, providing medical advice, appointment scheduling, and symptom analysis.
- Examples: Platforms like Ada Health and Babylon Health use AI to guide patients through symptoms and recommend appropriate care.
- Benefits: Virtual assistants reduce the burden on healthcare providers, improve patient engagement, and increase access to healthcare services.
F. Robotic Surgeries
AI and robotics combine to assist surgeons with minimally invasive procedures. Robots powered by AI provide enhanced precision, control, and efficiency.
- Example: The da Vinci Surgical System allows surgeons to perform complex procedures with improved accuracy and shorter recovery times for patients.
- Benefits: AI reduces surgical complications, improves accuracy, and accelerates post-operative recovery.
G. Administrative Automation
AI streamlines administrative tasks like appointment scheduling, billing, and managing medical records.
- Example: Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools automate medical transcription, while AI chatbots streamline appointment scheduling.
- Benefits: Administrative automation reduces operational costs, enhances workflow efficiency, and allows healthcare staff to focus on patient care.
III. Benefits of AI in Healthcare
AI offers numerous benefits that are transforming the healthcare industry by improving patient care, enhancing efficiency, and reducing costs:
1. Improved Diagnostic Accuracy
AI-powered tools analyze medical data, such as imaging scans, lab results, and clinical notes, with precision that often surpasses human capabilities. For instance, AI algorithms can detect cancers, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological disorders at early stages, enabling timely interventions and improving outcomes.
2. Enhanced Operational Efficiency
AI automates repetitive and time-consuming tasks, such as medical record management, billing, and appointment scheduling. This simplifies workflows, alleviates administrative burdens, and enables healthcare professionals to concentrate on patient care.
3. Cost Savings
By accelerating drug discovery, reducing diagnostic errors, and optimizing resource utilization, AI significantly lowers healthcare costs. Predictive analytics also help prevent costly complications by identifying risks early.
4. Personalized Treatment Plans
AI enables precision medicine by analyzing genetic, clinical, and lifestyle data to tailor treatments to individual patients. This approach boosts treatment effectiveness while minimizing side effects.
5. Improved Patient Outcomes
With AI’s ability to predict disease progression, monitor chronic conditions, and recommend optimal treatments, patients experience better care and improved health outcomes.
6. Increased Accessibility to Healthcare
AI-powered telemedicine platforms and virtual health assistants expand access to care, especially in remote or underserved areas. Patients can consult specialists, receive diagnoses, and monitor their health without visiting hospitals.
7. Real-Time Monitoring and Insights
Wearable devices and AI-driven tools continuously monitor patients’ vitals, providing real-time insights and alerting healthcare providers to potential health issues. This facilitates proactive care and reduces hospital readmissions.
In summary, AI enhances healthcare delivery by improving accuracy, efficiency, and accessibility while driving down costs and delivering better patient outcomes.
IV. Challenges of Implementing AI in Healthcare
✧ Data Privacy and Security
Healthcare data is sensitive, and AI systems rely heavily on patient data for training and predictions. Ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR is crucial to protect patient confidentiality.
- Solution: Implement robust data encryption, secure storage, and decentralized AI systems to mitigate security risks.
✧ Bias in AI Algorithms
AI systems may exhibit bias if trained on incomplete or non-representative datasets. Biased AI can lead to incorrect diagnoses, particularly for minority or underserved populations.
- Solution: Developers must ensure diverse and representative datasets and continually test algorithms for fairness and accuracy.
✧ Integration with Existing Systems
Healthcare providers frequently rely on legacy systems that may struggle to integrate smoothly with AI technologies. This hampers AI adoption and scalability.
- Solution: Gradual system upgrades, interoperability standards, and cloud-based solutions can facilitate smooth integration.
✧ Regulatory and Ethical Challenges
The adoption of AI raises ethical concerns about patient consent, accountability, and data ownership. Additionally, AI tools must undergo rigorous testing to comply with regulatory standards.
- Solution: Clear guidelines, ethical frameworks, and standardized regulatory approvals are essential for responsible AI implementation.
✧ Workforce Disruption
AI may replace some traditional healthcare roles, raising concerns about job losses.
- Solution: Training healthcare professionals to work alongside AI tools ensures a balance between automation and human expertise.
V. The Future of AI in Healthcare
The future of AI in healthcare promises groundbreaking advancements that will redefine how medical services are delivered, making them more efficient, accurate, and accessible. AI-driven technologies are already transforming diagnostics, treatment planning, and patient care, laying the groundwork for a smarter healthcare ecosystem.
AI excels in analyzing vast datasets, identifying patterns, and making predictions that far exceed human capabilities. Machine learning algorithms are being used to detect diseases like cancer at earlier stages through advanced imaging analysis, such as AI-powered radiology and pathology tools. These technologies reduce diagnostic errors and enable quicker interventions, saving lives and enhancing care quality. Similarly, predictive analytics allow healthcare providers to forecast patient outcomes, anticipate disease progression, and optimize treatment plans.
In personalized medicine, AI customizes treatments to align with an individual’s genetics, lifestyle, and medical history. Drug discovery, another critical area, is being revolutionized by AI algorithms that can simulate clinical trials and identify potential drug candidates much faster and at a lower cost. This innovation accelerates the creation of life-saving treatments, especially for rare diseases.
Remote patient monitoring through AI-powered wearable devices enables real-time tracking of vital signs, providing proactive care for patients. Telemedicine and virtual health assistants, driven by natural language processing, are bridging gaps in healthcare access, particularly in underserved or rural areas.
Despite its promise, AI adoption in healthcare faces challenges. Issues like data privacy, ethical concerns, regulatory frameworks, and the need for integration with existing systems must be addressed. Moreover, building trust among patients and healthcare professionals is essential to ensure the effective collaboration between humans and AI.
Looking ahead, AI will not replace healthcare professionals but rather enhance their capabilities. By automating administrative tasks, improving diagnostic precision, and offering data-driven insights, AI allows medical staff to focus more on patient interaction and critical decision-making. The future of AI in healthcare is one of collaboration, innovation, and improved outcomes—ultimately transforming the way healthcare is delivered and experienced globally.
VI. Case Studies of AI in Healthcare
1. DeepMind’s AI for Eye Disease Diagnosis
DeepMind developed an AI system capable of analyzing retinal scans to detect over 50 eye diseases. This technology has the potential to prevent vision loss through early detection.
2. IBM Watson for Oncology
IBM Watson uses AI to provide oncologists with treatment recommendations based on patient records and medical literature. It streamlines decision-making and improves treatment precision.
3. AI in COVID-19 Management
During the COVID-19 pandemic, AI played a vital role in predicting infection trends, identifying high-risk patients, and accelerating vaccine discovery. AI tools analyzed CT scans to detect COVID-19 pneumonia in real time.
VII. Conclusion
AI is primed to revolutionize healthcare by improving diagnosis, treatment, and patient care. From medical imaging to personalized medicine, AI’s applications are vast and transformative. While challenges like data privacy, bias, and integration persist, the future of AI in healthcare holds immense promise.
By fostering collaboration among healthcare professionals, AI developers, and policymakers, we can create a healthcare system that is more efficient, accurate, and accessible. As AI technologies continue to evolve, they will play an increasingly central role in delivering high-quality care and improving global health outcomes.